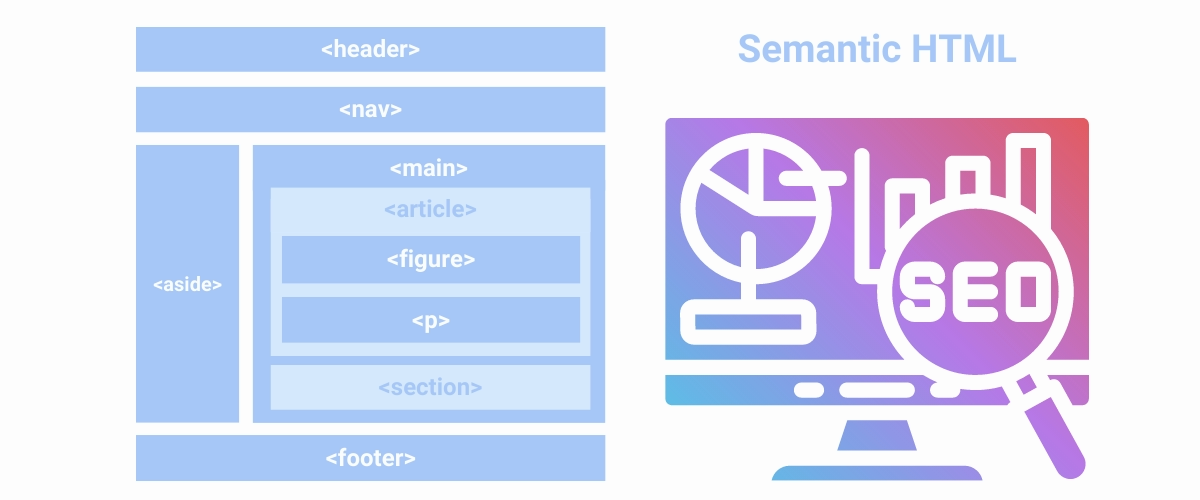
HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language)
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the markup language that forms the structure of web pages. At the core of every page you see on the internet, there is HTML. Web browsers read HTML code to display text, images, links, and other content on the screen.
Basic Features of HTML
- It is a markup language, meaning it uses tags (like
p,div,section) to define content rather than commands. - It defines the structure, not the appearance. (CSS is used for styling.)
- It is used to define elements such as text, images, links, tables, and forms.
- Web browsers (like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.) read these tags and display the content appropriately to the user.
The <html> Tag
In HTML architecture, the <html> tag is the container for all other elements that make up a web page.
The <html> tag should only contain two direct child elements: <head> and <body>. All other elements must be placed within either the <head> or the <body> tags.
The <html> tag should only contain two direct child elements: <head> and <body>. All other elements must be placed within either the <head> or the <body> tags.Meaning of HTML Tags
| HTML Tag | Meaning | HTML Tag | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| <html> | Hyper Text Markup Language | <q> | Quote |
| <p> | Paragraph | <h1>…<h6> | Heading 1…6 |
| <li> | List Item | <var> | Variable |
| <ol> | Ordered List | <nav> | Navigation |
| <ul> | Unordered List | <img> | Image |
| <em> | Emphasis | <sup> | Superscript |
| <a> | Anchor | <sub> | Subscript |
| <b> | Bold | <del> | Delete |
| <u> | Underline | <cite> | Citation Element |
| <i> | Italic | <s> | Strikethrough |
| <hr> | Horizontal Rule | <abbr> | Abbreviation / Acronym |
| <svg> | Scalable Vector Graphic | <blockquote> | Block Quote |
Block-Level Elements
Block-level HTML elements are those that create a new block or a structural segment on the web page. These elements typically occupy the full width available, which means they start on a new line and stretch out to the left and right as far as they can. This behavior is different from inline elements, which only take up as much width as necessary and do not start on a new line.
- <h1>
- <h2>
- <h3>
- <h4>
- <h5>
- <h6>
- <div>
- <ol>
- <ul>
- <li>
- <nav>
- <footer>
- <p>
- <hr>
- <blockquote>
- <address>
- <table>
- <thead>
- <tbody>
- <tfoot>
- <tr>
- <td>
- <th>
- <article>
- <aside>
- <section>
Inline-Level Elements
Inline-level elements in HTML are elements that do not start on a new line and only take up as much width as necessary. They can be nested within block-level elements and other inline elements without breaking the flow of the content. Unlike block-level elements, inline elements do not create a new block on the page.
- <a>
- <span>
- <img>
- <strong>
- <em>
- <b>
- <i>
- <u>
- <abbr>
- <cite>
- <code>
- <small>
- <sub>
- <sup>
- <mark>
- <time>
- <s>