Meta Title Tag | Title Optimization for SEO
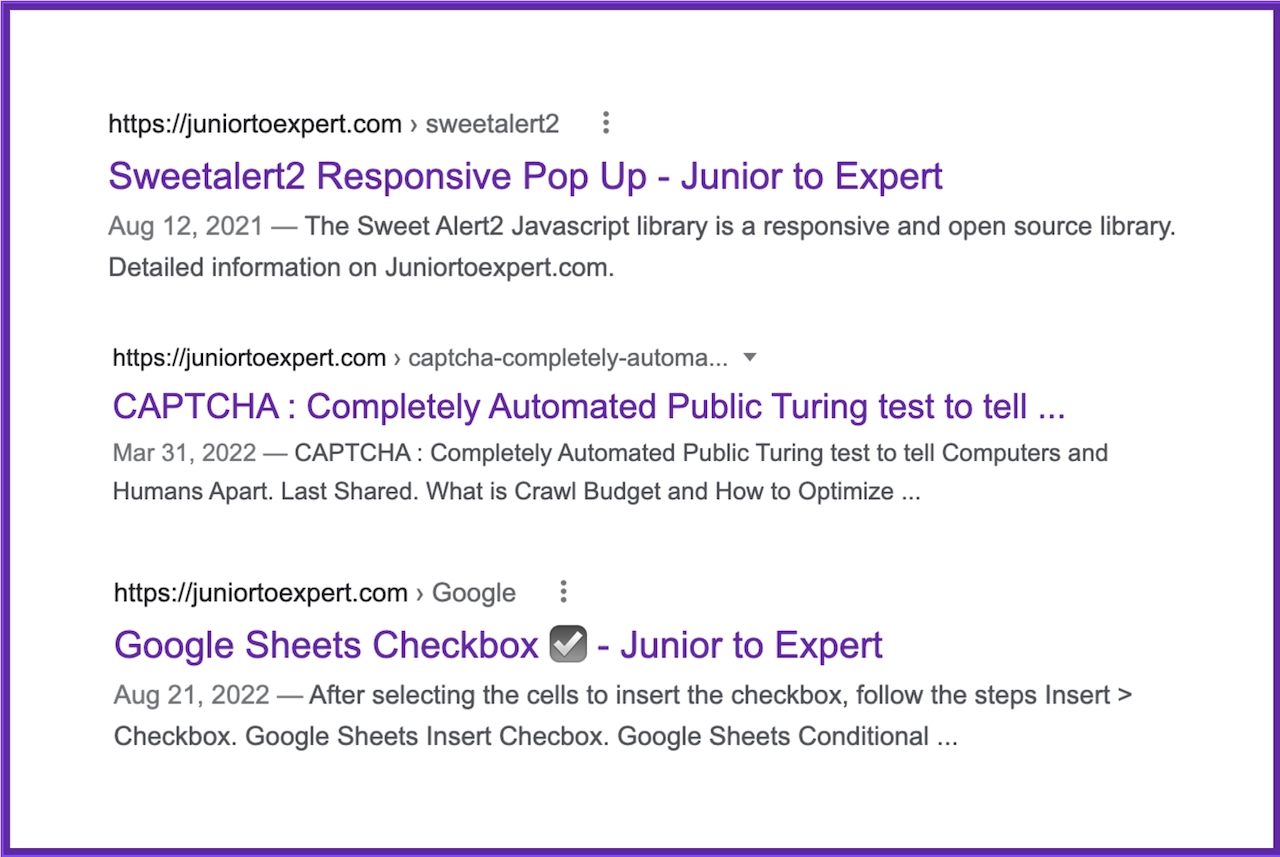
Search engines use the meta title tag (<title>) and a few other sources to generate the titles displayed on the search engine results page (SERP).
To increase visibility on search engines like Google, Yandex, and Bing, there are several important points to consider when optimizing page titles for SEO.
Things to Consider When Creating a Meta Title
Page-Specific Titles
Each page should have its specific <title> tag; identical titles should not be repeated across multiple pages.
Instead of using generic titles like “Home Page” for the homepage or “Archive” for category pages, use descriptive titles that define the page’s content.
Title Length
Do not make the <title> tags are unnecessarily long. Google does not set a strict character limit, but excessively long title tags may be truncated or modified to fit the display on the search results page.
As a general rule, aim for around 55–60 characters for your title tag. However, note that the actual limit depends on the pixel width of the characters used, not just the number of characters.


In a test meta title composed of 16 characters using both the letters “M” and “i”, the title with “M” measured 355.43 pixels in width, while the title using “i” measured only 87.77 pixels in width.
Since the pixel width occupied by the letter “M” is not the same as that of “i”, it’s better to use an average range of 55–60 characters for the <title> tag instead of a fixed number of characters.
Keyword Stuffing
Including relevant keywords in the page title is a good practice. However, avoid repeating the same words multiple times in the title. This practice is known as keyword stuffing, and it can appear spammy to both users and Google, potentially harming SEO performance.
Related SEO Topics